Use our heat pump operating cost calculator to determine your energy expenses based on the size of your home, heat pump capacity, operating hours, and local utility rate.
Daily Consumption: 0 kWh
Annual Consumption: 0 kWh
Daily Operating Costs: $0
Annual Operating Costs: $0
How to Determine Your Energy Expenses
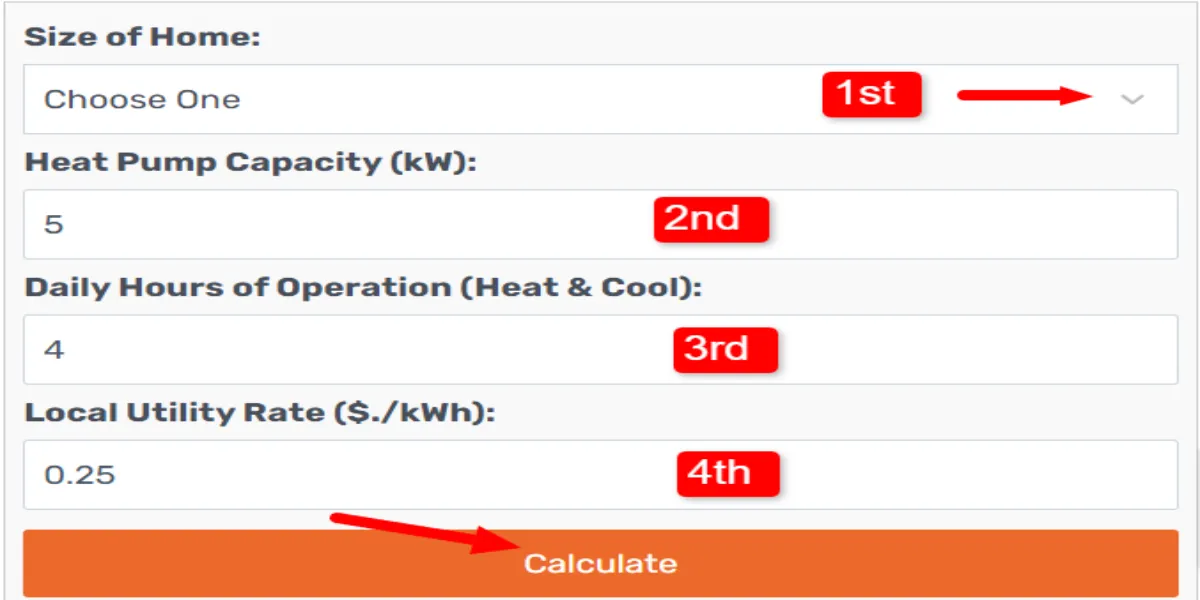
Here’s how you can effectively use a heat pump operating cost calculator to determine your energy expenses:
1. Input the Size of Your Home:
Start by selecting the size of your home from the options provided in the calculator.
Choose the range that best represents the square footage of your living space.
This information helps the calculator estimate the energy requirements based on the size of your home.
2. Specify the Heat Pump Capacity:
Enter the heat pump capacity in kilowatts (kW). This information is essential because the calculator needs to factor in the power output of your heat pump to determine the energy consumption accurately.
3. Determine the Daily Operating Hours:
Specify the number of hours your heat pump operates each day for both heating and cooling purposes.
Inputting the correct value is crucial for accurate calculations as it directly affects your daily energy consumption.
4. Enter the Local Utility Rate:
Input the local utility rate in dollars per kilowatt-hour ($/kWh).
This rate varies depending on your location and the specific utility provider.
It represents the cost you pay for each unit of energy consumed by your heat pump.
5. Calculate Your Daily Consumption:
Once you’ve provided all the necessary information, click the “Calculate” button.
The heat pump operating cost calculator will determine your daily consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) based on the heat pump capacity and daily operating hours.
6. Determine Your Annual Consumption:
The calculator will then multiply your daily consumption by 365 days to estimate your annual energy consumption.
This figure gives you an idea of the total energy usage for an entire year.
7. Calculate Your Daily Operating Costs:
Using the local utility rate and your daily consumption, the calculator will determine your daily operating costs.
This value represents the amount of money you can expect to spend each day to operate your heat pump.
8. Estimate Your Annual Operating Costs:
To determine your annual operating costs, the calculator multiplies your daily operating costs by 365 days.
This calculation provides an estimate of the total amount you can expect to spend on energy for your heat pump throughout the year.
Energy Consumption and Heat Pump Ratings:
Here, we will explore the key factors and steps involved in assessing energy consumption and heat pump ratings.
1. Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER):
The Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) is a measure of how efficiently a heat pump can cool a space.
It is calculated by dividing the cooling capacity (in British thermal units or BTUs) by the power consumption (in watts) of the heat pump.
A higher EER indicates better energy efficiency. When choosing a heat pump, look for a higher EER rating to ensure energy savings.
2. Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER):
The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) is similar to the EER, but it takes into account the varying temperatures throughout the year.
It measures the cooling output of a heat pump over an entire cooling season divided by the total energy consumed during that period.
The SEER rating provides a more accurate representation of a heat pump’s efficiency in real-world conditions.
Higher SEER ratings indicate better energy efficiency.
3. Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF):
The Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) measures the efficiency of a heat pump when it is operating in heating mode.
It is calculated by dividing the total heat output (in British thermal units or BTUs) during the heating season by the total electrical energy consumed (in watt-hours) during the same period.
A higher HSPF rating signifies better energy efficiency and cost savings during the heating season.
4. Coefficient of Performance (COP):
The Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a measure of the ratio of heating or cooling output to the electrical energy input of a heat pump.
It indicates the efficiency of the heat pump system as a whole, considering both energy consumption and heat transfer capabilities.
A higher COP value implies better energy efficiency and lower operating costs.
5. Energy Star Certification:
Energy Star is a voluntary program by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that identifies and promotes energy-efficient products.
When purchasing a heat pump, look for the Energy Star certification.
This label ensures that the heat pump meets or exceeds specific energy efficiency guidelines set by the EPA, resulting in energy savings and environmental benefits.
6. Sizing and Proper Installation:
To maximize energy efficiency and performance, it is crucial to properly size and install the heat pump.
Undersized or oversized heat pumps can lead to inefficient operation and increased energy consumption.
Consult with a qualified HVAC professional to determine the appropriate size of the heat pump based on your home’s heating and cooling needs.
7. Regular Maintenance and Operation:
Regular maintenance and proper operation of the heat pump are essential for optimal energy efficiency.
Keep the heat pump’s filters clean, clear debris around the outdoor unit, and ensure proper airflow.
Set the thermostat to energy-saving temperatures and avoid frequent temperature adjustments.
These practices help maintain efficient operation and reduce energy consumption.
Factors Affecting Heat Pump Efficiency:
Several factors influence the efficiency of a heat pump:
1. Temperature Difference:
The temperature difference between the heat source (e.g., outdoor air, ground, or water) and the desired indoor temperature significantly impacts heat pump efficiency.
As the temperature difference increases, the heat pump needs to work harder, reducing its efficiency.
Therefore, maintaining a moderate temperature difference helps improve efficiency.
2. Size and Capacity:
Properly sizing the heat pump according to the heating or cooling load of the space is vital for optimal efficiency.
Oversized heat pumps may short cycle, leading to frequent starts and stops, which decrease efficiency.
Undersized units may struggle to meet the demand, resulting in longer run times and reduced efficiency.
It’s essential to consult a professional to determine the appropriate size and capacity for your specific needs.
3. Insulation and Air Sealing:
Good insulation and air sealing in the building envelope help minimize heat loss or gain, reducing the workload on the heat pump.
Adequate insulation in walls, floors, and attics, along with properly sealed windows, doors, and ductwork, create a more efficient thermal envelope.
This enables the heat pump to maintain the desired indoor temperature more effectively.
4. Thermostat Settings:
Setting the thermostat at appropriate temperatures can significantly impact heat pump efficiency.
During winter, it is recommended to set the thermostat to lower temperatures (around 68°F) when occupants are away or asleep.
Raising the thermostat by a few degrees in summer can also help conserve energy.
Programmable or smart thermostats allow for automated temperature adjustments, optimizing comfort and efficiency.
5. Regular Maintenance:
Routine maintenance is crucial for ensuring optimal heat pump efficiency.
Regularly clean or replace filters to maintain proper airflow, as clogged filters can restrict airflow and reduce efficiency.
Additionally, schedule professional maintenance to check refrigerant levels, inspect components, and address any issues promptly.
Well-maintained heat pumps operate more efficiently and have a longer lifespan.
6. Climate Conditions:
The local climate plays a significant role in heat pump efficiency.
Air-source heat pumps, for example, may experience reduced efficiency in extremely cold climates.
Supplemental heating sources or geothermal heat pumps can be considered for regions with prolonged sub-freezing temperatures.
Understanding the specific climate conditions and selecting the appropriate heat pump type can optimize efficiency.
7. Ventilation and Airflow:
Proper ventilation and airflow within the building are crucial for maximizing heat pump efficiency.
Ensure that supply and return air registers are unobstructed by furniture or other objects.
Properly designed and balanced ductwork allows for efficient air distribution throughout the space.
Good airflow helps maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduces the workload on the heat pump.
Tips to Maximize Heat Pump Efficiency:
1. Properly Size Your Heat Pump:
One of the key factors in maximizing heat pump efficiency is ensuring that it is properly sized for your space.
The size of the heat pump should match the heating and cooling needs of your home or building.
A heat pump that is too small will struggle to heat or cool the space effectively, while an oversized heat pump will cycle on and off frequently, leading to inefficient operation.
Consult with a professional HVAC contractor to determine the right size for your heat pump based on factors such as square footage, insulation, and climate conditions.
2. Maintain Optimal Airflow:
Maintaining proper airflow is essential for optimal heat pump efficiency.
Clear any obstructions around the outdoor unit, such as leaves, debris, or shrubs, to ensure adequate airflow.
Additionally, regularly clean or replace air filters as instructed by the manufacturer.
Clogged filters restrict airflow, forcing the heat pump to work harder and consume more energy.
By keeping the airflow unrestricted, you can maximize the heat pump’s efficiency and reduce energy consumption.
3. Set Thermostat Temperatures Wisely:
Using your thermostat wisely can significantly impact heat pump efficiency.
During the heating season, set the thermostat to the lowest comfortable temperature.
For cooling, set it to the highest comfortable temperature.
Avoid extreme temperature settings that force the heat pump to work harder than necessary.
Consider using a programmable thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures based on your schedule, optimizing efficiency when you’re away or sleeping.
4. Ensure Proper Insulation:
Proper insulation plays a crucial role in heat pump efficiency.
Insulate your home or building effectively to minimize heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer.
Check for gaps or leaks around windows, doors, and other areas where air can escape.
Seal these gaps with weatherstripping or caulking to prevent heat transfer.
Well-insulated spaces allow the heat pump to operate more efficiently by reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling.
5. Use Zone Heating and Cooling:
Zone heating and cooling can further maximize heat pump efficiency by allowing you to heat or cool specific areas of your home as needed.
Instead of maintaining a uniform temperature throughout the entire house, zone heating and cooling systems use dampers and thermostats to control temperatures in different zones independently.
This way, you can concentrate the heat or cooling where it’s needed most, saving energy by not conditioning unoccupied areas.
6. Regular Maintenance and Tune-Ups:
Regular maintenance and tune-ups are essential for maximizing heat pump efficiency and prolonging its lifespan.
Schedule professional maintenance at least once a year, ideally before the start of the heating or cooling season.
A qualified technician will inspect and clean the heat pump, check refrigerant levels, lubricate moving parts, and identify any potential issues.
Proper maintenance ensures that your heat pump operates at its peak efficiency, saving energy and reducing the risk of breakdowns.
7. Consider Supplemental Heating:
In areas with extremely cold winters, a heat pump may struggle to provide sufficient heat on its own.
Consider supplementing your heat pump with an alternative heating source, such as a furnace or electric heaters, to ensure comfort during colder periods.
FAQs
What Is A Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator?
How Does The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator Work?
It then calculates the estimated cost of running your heat pump for a given period, such as per month or per year.
What Factors Affect The Operating Cost Of A Heat Pump?
Why Is It Important To Calculate The Operating Cost Of A Heat Pump?
This information can help you make informed decisions about energy usage, budgeting, and choosing the most cost-effective heating and cooling options for your home.
How Can I Use The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator?
The calculator will then provide you with an estimated operating cost for your heat pump.
Can The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator Be Used For Both Residential And Commercial Heat Pump Systems?
However, the specific electricity rates and usage patterns may vary between residential and commercial properties, so it’s important to input the correct information for accurate results.
How Accurate Is The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator?
The accuracy of the calculator depends on the accuracy of the input data and the assumptions used in the calculations.
It’s always a good idea to double-check the results with your actual electricity bills to ensure accuracy.
Is It Possible To Calculate The Operating Cost Of A Heat Pump For A Specific Period, Such As A Month Or A Year?
By inputting the number of hours per day the heat pump runs, the calculator can provide an estimated cost for the desired period.
Can The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator Factor In Additional Costs Associated With Heating Systems?
It does not factor in additional costs such as maintenance, repairs, or the initial cost of purchasing and installing the heat pump.
These additional costs should be considered separately when evaluating the overall cost of a heating system.
Can The Heat Pump Operating Cost Calculator Help Determine The Size Of The Heat Pump Needed For A Specific Space?
It does not directly determine the size of the heat pump needed for a specific space.
However, by calculating the operating cost for different heat pump sizes, you can compare the cost implications and make an informed decision on the appropriate size for your space.
Conclusion
Our heat pump operating cost calculator provides accurate estimates of your daily and annual energy consumption.
It also calculates your operating costs based on the size of your home, heat pump capacity, operating hours, and local utility rate.
With this information, you can make informed decisions about how to use your heat pump efficiently.
Additionally, the calculator helps you understand the various factors that influence energy efficiency, empowering you to optimize your energy usage and reduce costs.
