Our Natural Gas Pipe Size Calculator helps determine the appropriate pipe size for optimal water pressure, energy efficiency, and appliance performance.
Disclaimer: This calculator is provided for educational purposes only. It assists in estimating pipe size based on the criteria provided. It does not constitute professional advice or replace proper consultation for specific applications.
How to Use Our Natural Gas Pipe Size Calculator
Step 1: Select Pipe Size
- In the “Select Pipe Size” dropdown menu, choose the appropriate pipe size based on the options provided. The options are listed in inches (e.g., 1/2″, 3/4″, 1″, etc.).
- Once you’ve selected the pipe size, proceed to the next step.
Step 2: Select Pipe Length
- In the “Select Length” dropdown menu, choose the desired length of the pipe. Options are provided in feet (e.g., 10 ft, 20 ft, 30 ft, etc.).
- After selecting the pipe length, you’re ready to proceed to the next step.
Step 3: Calculate BTU
- Click the “Calculate” button. This will initiate the calculation process based on the chosen pipe size and length.
- The calculator will compute the BTU (British Thermal Unit) value for the selected pipe size and length.
Step 4: View Results
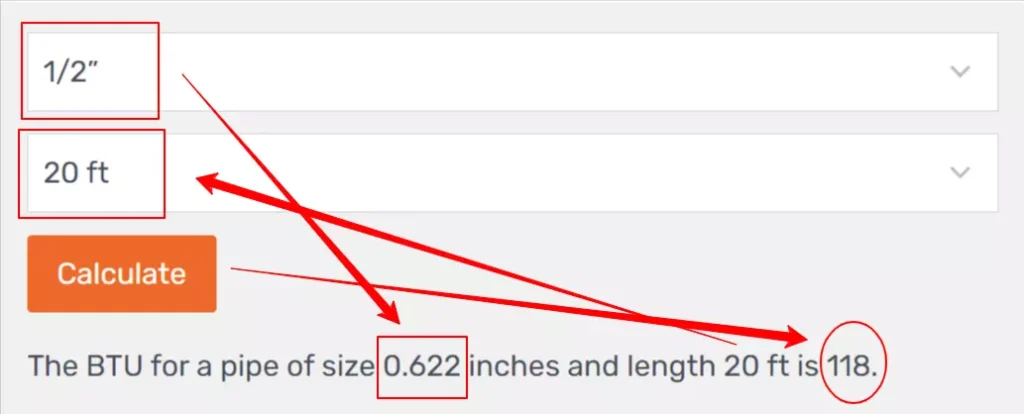
- Once the calculation is complete, the calculated BTU value will be displayed in the “output” section on the page.
- The BTU value indicates the heat output or capacity of the pipe, which is crucial for various applications.
Step 5: Interpretation and Use
- Interpret the BTU value to understand the pipe’s capacity in terms of heat output.
- Consider how this information aligns with your specific needs, such as water pressure, energy efficiency, and appliance performance.
Natural Gas Pipe Size Chart
| PIPE SIZE (inches) | Actual ID | 10 ft | 20 ft | 30 ft | 40 ft | 50 ft | 60 ft | 70 ft | 80 ft | 90 ft | 100 ft | 125 ft | 150 ft | 175 ft | 200 ft | 250 ft | 300 ft | 350 ft | 400 ft |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/2” | 0.622 | 172 | 118 | 95 | 81 | 72 | 65 | 60 | 56 | 52 | 50 | 44 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 30 | 27 | 25 | 23 |
| 3/4” | 0.824 | 360 | 247 | 199 | 170 | 151 | 137 | 126 | 117 | 110 | 104 | 92 | 83 | 77 | 71 | 63 | 57 | 53 | 49 |
| 1” | 1.049 | 678 | 466 | 374 | 320 | 284 | 257 | 237 | 220 | 207 | 195 | 173 | 157 | 144 | 134 | 119 | 108 | 99 | 92 |
| 1 1/4” | 1.380 | 1,390 | 957 | 768 | 657 | 583 | 528 | 486 | 452 | 424 | 400 | 355 | 322 | 296 | 275 | 244 | 221 | 203 | 189 |
| 1 1/2” | 1.610 | 2,090 | 1,430 | 1,150 | 985 | 873 | 791 | 728 | 677 | 635 | 600 | 532 | 482 | 443 | 412 | 366 | 331 | 305 | 283 |
| 2” | 2.067 | 4,020 | 2,760 | 2,220 | 1,900 | 1,680 | 1,520 | 1,400 | 1,300 | 1,220 | 1,160 | 1,020 | 928 | 854 | 794 | 704 | 638 | 587 | 546 |
| 2 1/2” | 2.469 | 6,400 | 4,400 | 3,530 | 3,020 | 2,680 | 2,430 | 2,230 | 2,080 | 1,950 | 1,840 | 1,630 | 1,480 | 1,360 | 1,270 | 1,120 | 1,020 | 935 | 870 |
| 3” | 3.068 | 11,300 | 7,780 | 6,250 | 5,350 | 4,740 | 4,290 | 3,950 | 3,670 | 3,450 | 3,260 | 2,890 | 2,610 | 2,410 | 2,240 | 1,980 | 1,800 | 1,650 | 1,540 |
| 4” | 4.026 | 23,100 | 15,900 | 12,700 | 10,900 | 9,660 | 8,760 | 8,050 | 7,490 | 7,030 | 6,640 | 5,890 | 5,330 | 4,910 | 4,560 | 4,050 | 3,670 | 3,370 | 3,140 |
Read the full guide about the Natural Gas Pipe Size Chart BTU here.
Why is Pipe Sizing Important?
Role in Water Pressure
Let’s start with water pressure. Imagine taking a shower with just a trickle of water. Not fun, right?
The size of the pipe can make that happen. If the pipe is too small, it can’t hold much water. This will lower the pressure. So, pipe size plays a big role in water pressure.
Water Quality and Pipe Size
Now let’s discuss water quality. Picture a clean, sparkling stream. The water flows freely.
But, if the pipe is too small, things change. Water gets stuck. This can lead to rust and bad taste. Size matters for clean water.
Pipe Longevity
Next, think about how long pipes last. We call this pipe longevity. The right size means less wear and tear.
Less stress on the pipe helps it last longer. A pipe that’s too small will work too hard. This makes it wear out faster.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is our next stop. Bigger isn’t always better. A pipe that’s too big will need more power to move water.
That’s like using a huge bucket to carry just one apple. You’d waste energy. So, the right pipe size helps save energy.
Impact on Appliances
Now, let’s look at your home appliances. Think about your dishwasher or washing machine.
They need a certain water flow. Get the pipe size wrong and these machines won’t work well. It’s like trying to fill a pool with a garden hose. It will take forever.
Cost Implications
Lastly, we need to consider the cost. Wrong pipe size can be expensive. Replacing pipes isn’t cheap.
So getting it right the first time saves money. Imagine buying shoes. If they don’t fit, you have to go back to the store. It’s the same with pipes.
Selecting Pipe Size: Factors to Consider
Pipe Material
First, let’s talk about pipe material. Different materials can affect water flow. For example, copper and PVC are common materials.
Copper is strong and lasts a long time. PVC is cheaper and easier to work with. But each has its own features that may be better for specific jobs.
Water Pressure
Next up is water pressure. It’s crucial for deciding pipe size. High water pressure needs stronger and larger pipes.
Low pressure may allow for smaller pipes. Measuring pressure is a step you can’t skip.
Water Flow Rate
Another key point is the water flow rate. This tells you how much water moves through the pipe.
Imagine a river. A wider river lets more water flow. The same goes for pipes.
A bigger pipe size allows more water to pass. So, for higher flow rates, choose a bigger pipe.
Pipe Length
Now consider pipe length. The longer the pipe, the more the water loses pressure. In a long pipe, water slows down.
It’s like when you try to run a long race. You get tired and slow down, right? So, a longer pipe might need to be wider to keep the water moving well.
Pipe Fittings and Turns
Don’t forget about pipe fittings and turns. Every time water turns a corner, it loses speed.
Think of it like a race car on a track. The car slows down to make a turn. More turns mean you may need a larger pipe to keep the water moving fast.
Temperature Factors
Last but not least, think about temperature. Hot water can affect some pipe materials. For example, PVC might not be good for very hot water. You need to know the water temperature to pick the right material and size.
Location and Accessibility
The location and accessibility of the pipe also play a role. Pipes hidden in walls are harder to replace.
So, they might need to be more durable. If a pipe is easy to reach, you might have more choices.
Risks of Incorrect Natural Gas Pipe Sizing
Low Pressure in the System
Low gas pressure is a big concern. This problem can happen if your pipes are too small.
Small pipes can’t handle the amount of gas you need. Imagine a highway with just one lane. Cars will slow down. In the same way, gas slows down in small pipes.
Wastage of Gas
Gas wastage is another risk. In systems with poorly sized pipes, gas may leak. Leaks are bad for two reasons.
First, they waste your money. You pay for gas you don’t use. Second, they’re not safe. Leaking gas can be dangerous.
Reduced Efficiency
When pipes are the wrong size, efficiency suffers. Your appliances won’t work at their best.
Imagine trying to drink a thick smoothie with a tiny straw. It’s hard work! Appliances feel the same stress with wrong-sized pipes.
Safety Hazards
Safety is the most critical issue. Incorrectly sized pipes may lead to accidents. Gas can leak and cause fires.
In extreme cases, explosions can occur. We don’t want that to happen. Always think of safety first.
Increased Costs
Wrong-sized pipes are costly. First, you may need to replace them. That’s expensive. Second, you pay more in energy bills.
Your system has to work harder than normal. This extra work costs you money every month.
Unreliable Supply
A gas supply that keeps stopping is unreliable. This happens when pipes are either too big or too small.
Pipes that are too big can’t keep pressure up. Pipes that are too small can’t supply enough gas. Either way, your supply won’t be steady.
Incomplete Combustion
Incomplete combustion is a problem you might not see. But you’ll feel its effects. It can create harmful gases.
These gases can harm your health over time. Imagine lighting only half of a campfire. The fire won’t keep you warm. Similarly, incomplete combustion won’t do its job well.
