Looking to choose the right wire for your project? Compare Copper vs Aluminum Wire Size Chart in our concise guide.
We’re breaking down the essentials, offering clear insights to help you select the best material with ease. Read on and find your perfect match!
Copper Vs Aluminum Wire Size Chart
| Wire Gauge Size | Copper 60°C (140°F) | Copper 75°C (167°F) | Copper 90°C (197°F) | Aluminum 75°C (167°F) | Aluminum 90°C (197°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 15 | 15 | 15 | – | – |
| 12 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 15 |
| 10 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 25 | 25 |
| 8 | 40 | 50 | 55 | 40 | 45 |
| 6 | 55 | 65 | 75 | 50 | 55 |
| 4 | 70 | 85 | 95 | 65 | 75 |
| 3 | 85 | 100 | 115 | 75 | 85 |
| 2 | 95 | 115 | 130 | 90 | 100 |
| 1 | – | 130 | 145 | 100 | 115 |
| 1/0 | – | 150 | 170 | 120 | 135 |
| 2/0 | – | 175 | 195 | 135 | 150 |
| 3/0 | – | 200 | 225 | 155 | 175 |
| 4/0 | – | 230 | 260 | 180 | 205 |
| 250 | – | 255 | 290 | 205 | 230 |
| 300 | – | 285 | 320 | 230 | 260 |
| 350 | – | 310 | 350 | 250 | 280 |
| 500 | – | 380 | 430 | 310 | 350 |
| 600 | – | 420 | 475 | 340 | 385 |
| 750 | – | 475 | 535 | 385 | 435 |
| 1000 | – | 545 | 615 | 445 | 500 |
The chart includes the maximum ampacity values (current-carrying capacity) for different types of wires and temperature conditions.
The wire sizes are categorized based on the American Wire Gauge (AWG) standard.
Here’s a breakdown of the information provided in the chart:
Wire Gauge Size
This column lists the different wire gauge sizes, ranging from 14 AWG to 1000 kcmil.
Copper 60ºC (140ºF) – NM-B, UF-B
These values represent the maximum ampacity of copper wires with a temperature rating of 60°C (140°F), used in applications like NM-B (Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable) and UF-B (Underground Feeder Cable).
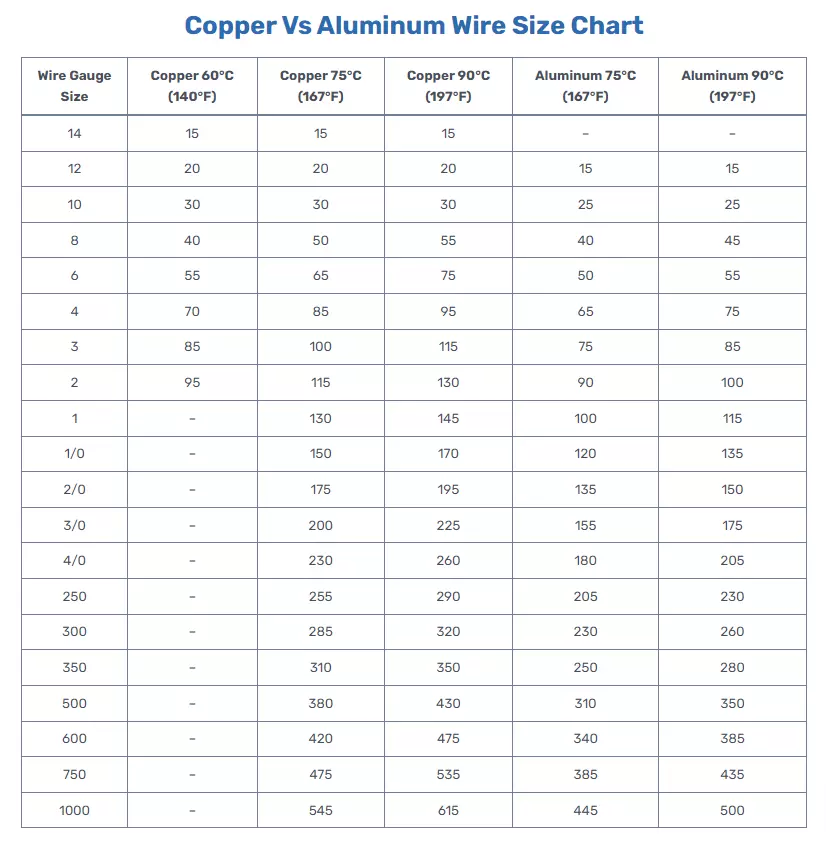
Copper 75ºC (167ºF) – THW, THWN, SE, USE, XHHW
These values represent the maximum ampacity of copper wires with a temperature rating of 75°C (167°F), used in applications like THW, THWN, SE (Service Entrance Cable), USE (Underground Service Entrance Cable), and XHHW (Cross-Linked Polyethylene High-Temperature Water Resistant Cable).
Copper 90ºC (197ºF) – THWN-2, THHN, XHHW-2
These values represent the maximum ampacity of copper wires with a temperature rating of 90°C (197°F), used in applications like THWN-2, THHN, and XHHW-2.
Aluminum 75ºC (167ºF) – THW, THWN, SE, USE, XHHW
These values represent the maximum ampacity of aluminum wires with a temperature rating of 75°C (167°F), used in applications like THW, THWN, SE, USE, and XHHW.
Aluminum 90ºC (197ºF) – XHHW-2, THHN, TWHN-2
These values represent the maximum ampacity of aluminum wires with a temperature rating of 90°C (197°F), used in applications like XHHW-2, THHN, and TWHN-2.
The ampacity values indicate the maximum safe current-carrying capacity of the wires without exceeding their temperature ratings and safety standards.
Different Factors Influencing Wire Size Selection

Conductivity and Resistance
Copper’s amazing conductivity means it’s like a superstar at letting electricity flow smoothly.
When you need power to move without any hiccups, copper is your go-to.
On the flip side, aluminum faces a challenge with higher resistance.
Imagine it as a narrow road where the electric current has to push harder to get through.
That’s why aluminum wires need to be thicker to handle the same amount of electricity as copper.
Weight and Cost
Imagine carrying a feather versus lugging around a brick. Aluminum wins the weight contest, making it easier to handle during installation.
On the other hand, copper is the heavyweight champion, which might require more muscle when installing.
Now, let’s talk about the budget. Copper does come with a higher cost.
It’s like choosing between a regular phone and the latest premium model – both have their perks, but one’s pricier.
Corrosion Resistance
Copper is a true hero when it comes to fighting corrosion. It’s like wearing armor that keeps rust at bay.
So, if your wires are going to face rain and wind, copper is your trusty sidekick. But aluminum isn’t as lucky.
It’s more like a car that rusts quickly in salty air. If exposed to the wrong conditions, aluminum wires might need extra protection.
Thermal Expansion
Think about a hot summer day when everything seems to expand. Aluminum takes this expansion thing to the next level.
It stretches more than copper when it gets hot. Imagine one friend who always seems to be growing taller under the sun while the other stays the same height.
Copper, on the other hand, is pretty stable. It doesn’t change much with temperature swings.
Ampacity Ratings
Picture this: a wire’s ability to carry current is like its superhero power. We call it ampacity, and it’s vital for safety.
Just like a weight limit in an elevator, each wire size has a maximum current it can handle without getting overwhelmed.
Using a wire with lower ampacity for a high current load is like trying to fit too many people in a small elevator. The results might not be pleasant!
Copper Wire Advantages

Conductivity
When it comes to conductivity, copper truly shines. This highly conductive material lets electricity glide through it with ease, offering minimal resistance.
The result? A consistent and smooth performance that ensures your electrical system’s reliability.
Performance
Speaking of performance, copper wires are your go-to choice for stability.
Performance isn’t something to gamble on, and with copper, you’re securing an unswerving connection.
Corrosion Resistance
Have you considered the environment’s impact on your wiring? With copper’s impressive corrosion resistance, worry no more.
Outdoor conditions or harsh environments, copper stands tall against the elements.
Stability
Now, let’s talk about stability. With minimal thermal expansion, copper maintains its shape and size through temperature changes.
That means a safer, long-lasting connection that you can rely on.
Copper Wire Disadvantages
Weight
Sure, copper has its drawbacks. One of them is its weight. Heavier wires can be trickier to install.
But remember, that’s a small price to pay for its many benefits.
Cost
The cost of copper can indeed be higher. But think of it as an investment in quality and reliability. You’re getting what you pay for.
Limited Ampacity
Although copper’s ampacity might be lower than aluminum, it’s about finding the right fit for your needs.
Consider your current-carrying requirements, and copper may still be the superior choice.
Availability
Lastly, the availability of copper might fluctuate. But isn’t a precious resource often worth the effort? Its finite nature just underscores its value.
Aluminum Wire Advantages

Weight
When it comes to weight, aluminum takes the lead. Lighter and more manageable, it’s the choice for easy handling and installation. Ease your work without compromising too much on quality.
Cost
Looking to cut down on expenses? Aluminum’s cost-effectiveness is an attractive option.
Affordable without forsaking all the essential qualities, it’s worth considering.
Ampacity
Now, here’s where aluminum really shines. Its ampacity or current-carrying capacity is remarkable.
Need more power? Aluminum might just be your answer.
Thermal Expansion
Aluminum’s thermal expansion can be a unique advantage in specific applications.
Flexibility where you need it – that’s aluminum for you.
Aluminum Wire Disadvantages
Conductivity
But wait, there are caveats. Aluminum’s conductivity isn’t as great as copper’s.
That can lead to more energy loss. Is that a trade-off you’re willing to make?
Corrosion Susceptibility
And don’t forget about corrosion. Unlike copper, aluminum can corrode more easily.
Think about the long-term health of your connections.
Durability
When it comes to durability, aluminum might fall short. More prone to breakage or fatigue, it might not be as resilient.
Ensure it fits your application’s demands.
Compatibility Issues
Finally, consider the compatibility issues. Aluminum may not play well with copper-specific devices or connectors.
Be mindful of integration, or you might face challenges down the road.
FAQs
Is copper or aluminum wire better for electrical wiring?
Copper is denser, more conductive, and more flexible, while aluminum is lighter, less expensive, and can oxidize over time.
Why would I choose an aluminum wire over copper?
Aluminum is generally cheaper and lighter, making it a good choice for high-voltage transmission over long distances.
Do copper and aluminum wires connect directly?
No, direct connections can cause galvanic corrosion. Special connectors or techniques, like bimetallic lugs, are used to join them safely.
How do I compare wire sizes between copper and aluminum?
Copper Vs Aluminum Wire Size Charts help in determining the appropriate wire gauge for each metal based on the current load.
Are there any special considerations when installing aluminum wiring?
Yes, aluminum can oxidize, so it’s essential to use anti-oxidant compounds at connections. Also, because it’s less flexible, care is needed to prevent breakage during installation.
Final Words
In this exploration of the Copper vs. Aluminum wire debate, we’ve unveiled the critical factors shaping your choice.
Conductivity, cost, corrosion resistance, and more – each element plays a role in crafting your electrical system’s efficiency and reliability.
Armed with the insights from our comprehensive analysis, you’re now equipped to make an informed decision that suits your unique needs.
As you embark on your wiring journey, remember, it’s not just about wires; it’s about empowering your home’s electrical foundation.

